Multisets¶
This chapter describes functions for creating and manipulating multisets. A
multiset  is represented by an array of
is represented by an array of 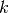 integers in the range
0 to
integers in the range
0 to 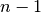 , where each value
, where each value 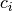 may occur more than once. The
multiset
may occur more than once. The
multiset  corresponds to indices of
corresponds to indices of 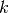 elements chosen from an
elements chosen from an
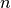 element vector with replacement. In mathematical terms,
element vector with replacement. In mathematical terms, 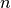 is
the cardinality of the multiset while
is
the cardinality of the multiset while 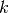 is the maximum multiplicity of
any value. Multisets are useful, for example, when iterating over the indices
of a
is the maximum multiplicity of
any value. Multisets are useful, for example, when iterating over the indices
of a 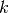 -th order symmetric tensor in
-th order symmetric tensor in 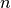 -space.
-space.
The functions described in this chapter are defined in the header file
gsl_multiset.h.
The Multiset struct¶
-
type gsl_multiset¶
A multiset is defined by a structure containing three components, the values of
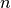 and
and 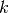 , and a pointer to the multiset array.
The elements of the multiset array are all of type
, and a pointer to the multiset array.
The elements of the multiset array are all of type size_t, and are stored in increasing order. Thegsl_multisetstructure looks like this:typedef struct { size_t n; size_t k; size_t *data; } gsl_multiset;
Multiset allocation¶
-
gsl_multiset *gsl_multiset_alloc(size_t n, size_t k)¶
This function allocates memory for a new multiset with parameters
n,k. The multiset is not initialized and its elements are undefined. Use the functiongsl_multiset_calloc()if you want to create a multiset which is initialized to the lexicographically first multiset element. A null pointer is returned if insufficient memory is available to create the multiset.
-
gsl_multiset *gsl_multiset_calloc(size_t n, size_t k)¶
This function allocates memory for a new multiset with parameters
n,kand initializes it to the lexicographically first multiset element. A null pointer is returned if insufficient memory is available to create the multiset.
-
void gsl_multiset_init_first(gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function initializes the multiset
cto the lexicographically first multiset element, i.e.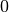 repeated
repeated 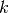 times.
times.
-
void gsl_multiset_init_last(gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function initializes the multiset
cto the lexicographically last multiset element, i.e.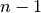 repeated
repeated 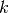 times.
times.
-
void gsl_multiset_free(gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function frees all the memory used by the multiset
c.
-
int gsl_multiset_memcpy(gsl_multiset *dest, const gsl_multiset *src)¶
This function copies the elements of the multiset
srcinto the multisetdest. The two multisets must have the same size.
Accessing multiset elements¶
The following function can be used to access the elements of a multiset.
-
size_t gsl_multiset_get(const gsl_multiset *c, const size_t i)¶
This function returns the value of the
i-th element of the multisetc. Ifilies outside the allowed range of 0 to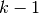 then the error handler is invoked and 0 is returned. An inline version of this function is used when
then the error handler is invoked and 0 is returned. An inline version of this function is used when HAVE_INLINEis defined.
Multiset properties¶
-
size_t gsl_multiset_n(const gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function returns the range (
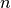 ) of the multiset
) of the multiset c.
-
size_t gsl_multiset_k(const gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function returns the number of elements (
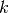 ) in the multiset
) in the multiset c.
-
size_t *gsl_multiset_data(const gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function returns a pointer to the array of elements in the multiset
c.
-
int gsl_multiset_valid(gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function checks that the multiset
cis valid. Thekelements should lie in the range 0 to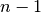 , with each
value occurring in nondecreasing order.
, with each
value occurring in nondecreasing order.
Multiset functions¶
-
int gsl_multiset_next(gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function advances the multiset
cto the next multiset element in lexicographic order and returnsGSL_SUCCESS. If no further multisets elements are available it returnsGSL_FAILUREand leavescunmodified. Starting with the first multiset and repeatedly applying this function will iterate through all possible multisets of a given order.
-
int gsl_multiset_prev(gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function steps backwards from the multiset
cto the previous multiset element in lexicographic order, returningGSL_SUCCESS. If no previous multiset is available it returnsGSL_FAILUREand leavescunmodified.
Reading and writing multisets¶
The library provides functions for reading and writing multisets to a file as binary data or formatted text.
-
int gsl_multiset_fwrite(FILE *stream, const gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function writes the elements of the multiset
cto the streamstreamin binary format. The function returnsGSL_EFAILEDif there was a problem writing to the file. Since the data is written in the native binary format it may not be portable between different architectures.
-
int gsl_multiset_fread(FILE *stream, gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function reads elements from the open stream
streaminto the multisetcin binary format. The multisetcmust be preallocated with correct values of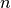 and
and 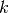 since the
function uses the size of
since the
function uses the size of cto determine how many bytes to read. The function returnsGSL_EFAILEDif there was a problem reading from the file. The data is assumed to have been written in the native binary format on the same architecture.
-
int gsl_multiset_fprintf(FILE *stream, const gsl_multiset *c, const char *format)¶
This function writes the elements of the multiset
cline-by-line to the streamstreamusing the format specifierformat, which should be suitable for a type ofsize_t. In ISO C99 the type modifierzrepresentssize_t, so"%zu�n"is a suitable format 1. The function returnsGSL_EFAILEDif there was a problem writing to the file.
-
int gsl_multiset_fscanf(FILE *stream, gsl_multiset *c)¶
This function reads formatted data from the stream
streaminto the multisetc. The multisetcmust be preallocated with correct values of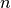 and
and 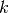 since the function uses the size of
since the function uses the size of cto determine how many numbers to read. The function returnsGSL_EFAILEDif there was a problem reading from the file.
Examples¶
The example program below prints all multisets elements containing the values
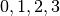 ordered by size. Multiset elements of the same size are
ordered lexicographically.
ordered by size. Multiset elements of the same size are
ordered lexicographically.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_multiset.h>
int
main (void)
{
gsl_multiset * c;
size_t i;
printf ("All multisets of {0,1,2,3} by size:\n") ;
for (i = 0; i <= 4; i++)
{
c = gsl_multiset_calloc (4, i);
do
{
printf ("{");
gsl_multiset_fprintf (stdout, c, " %u");
printf (" }\n");
}
while (gsl_multiset_next (c) == GSL_SUCCESS);
gsl_multiset_free (c);
}
return 0;
}
Here is the output from the program,
All multisets of {0,1,2,3} by size:
{ }
{ 0 }
{ 1 }
{ 2 }
{ 3 }
{ 0 0 }
{ 0 1 }
{ 0 2 }
{ 0 3 }
{ 1 1 }
{ 1 2 }
{ 1 3 }
{ 2 2 }
{ 2 3 }
{ 3 3 }
{ 0 0 0 }
{ 0 0 1 }
{ 0 0 2 }
{ 0 0 3 }
{ 0 1 1 }
{ 0 1 2 }
{ 0 1 3 }
{ 0 2 2 }
{ 0 2 3 }
{ 0 3 3 }
{ 1 1 1 }
{ 1 1 2 }
{ 1 1 3 }
{ 1 2 2 }
{ 1 2 3 }
{ 1 3 3 }
{ 2 2 2 }
{ 2 2 3 }
{ 2 3 3 }
{ 3 3 3 }
{ 0 0 0 0 }
{ 0 0 0 1 }
{ 0 0 0 2 }
{ 0 0 0 3 }
{ 0 0 1 1 }
{ 0 0 1 2 }
{ 0 0 1 3 }
{ 0 0 2 2 }
{ 0 0 2 3 }
{ 0 0 3 3 }
{ 0 1 1 1 }
{ 0 1 1 2 }
{ 0 1 1 3 }
{ 0 1 2 2 }
{ 0 1 2 3 }
{ 0 1 3 3 }
{ 0 2 2 2 }
{ 0 2 2 3 }
{ 0 2 3 3 }
{ 0 3 3 3 }
{ 1 1 1 1 }
{ 1 1 1 2 }
{ 1 1 1 3 }
{ 1 1 2 2 }
{ 1 1 2 3 }
{ 1 1 3 3 }
{ 1 2 2 2 }
{ 1 2 2 3 }
{ 1 2 3 3 }
{ 1 3 3 3 }
{ 2 2 2 2 }
{ 2 2 2 3 }
{ 2 2 3 3 }
{ 2 3 3 3 }
{ 3 3 3 3 }
All 70 multisets are generated and sorted lexicographically.
Footnotes
- 1
In versions of the GNU C library prior to the ISO C99 standard, the type modifier
Zwas used instead.